This article is for people who want to drive more organic search traffic from traditional Google search to their organization’s website as part of an overall content marketing strategy.
We commonly discover websites with dozens of blog posts but negligible organic traffic to that content.
The reason for this ‘low to no’ search traffic is simple. Today’s rules for getting found through online search were not implemented.
Even though the web is more ‘zero-click’ than ever as LLM results increasingly dominate search results, organic search results still matter for business growth in 2025.
Rule #1: Create original, helpful, people-first content throughout your website
Content that follows the rules can be permanent organizational assets, and it should be created and managed as such if the goal is to generate more website search traffic.
A Brief History of Search
Once upon a time, SEO (search engine optimization) was mainly about selecting the right keyword, a.k.a. keyphrase, and ensuring that a web page or blog post repeated that keyword often enough.
SEOs (search engine optimizers) would game the system using a practice called keyword stuffing.
The page or post with many keywords was more likely to rank high in the search engine results. This would, in turn, result in more visitors to a page or post on a website, enhancing a brand’s visibility.
But that was when Google’s and other search engine algorithms were not very sophisticated by today’s standards.
The processes for getting more people to find your website through search have gotten complicated.
This is partly because search engine algorithms have evolved. For example, rather than just scanning for a keyword and its variations, search engines use natural language understanding to interpret the meaning of many different words in a piece of content, much as a person would.
When Google’s SGE (Search Generative Experience) launches, the content Google prioritizes will likely shift once more.
Improving Website SEO
Achieving better SEO is the sum of many minor improvements — and sometimes a few major ones. A convenient feature of web properties you own is that changing existing content is always possible.
Let’s look at improving your website’s SEO in 2025 and beyond.
This may seem like a long list of considerations when creating content, but remember that Google has over 200 ranking factors.
Addressing little things will become second nature with practice.
Rule #2: Do all the little things right.
Use the ideas below to guide new content and update your website’s existing content. You can check Google Analytics and Google Search Console to see whether your efforts have resulted in more users visiting pages and posts you have updated and re-optimized.
Comply with Google’s guidance
Google has not wavered from its advice to content creators in over two decades. That advice is to “make pages for users, not for search engines.”
Google can be fooled by mediocre, 100% AI-generated content in the short term.
However, quality content should be the primary consideration for long-term results.
Involve SMEs (subject matter experts)
E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness) is part of Google’s Search Quality Rater Guidelines. This is the handbook that human raters use to evaluate the quality of search results.
Google’s September 2023 Helpful Content Update, which punished many niche sites and recipe bloggers, emphasized the Es in E-E-A-T.
Author and analyst Dr. Marie Haynes said, “Google wants to recommend content from people known for their expertise on a topic, not just marketers creating content.”
Ideally, content creators should write about things they have first-hand experience with. Alternatively, writers can interview and quote SMEs.
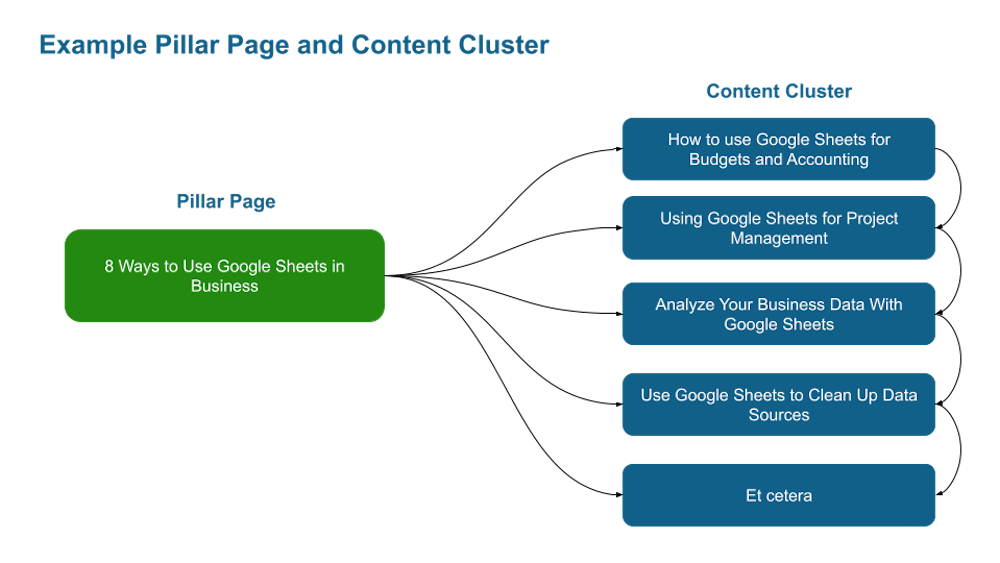
Create pillar pages and content clusters
Let’s say you sell a Google Sheets add-on for businesses.
Your pillar page could be “8 Ways to Use Google Sheets in Business.”
Your content cluster could then be detailed posts regarding those eight ways.
Use AI writers and chat apps judiciously
It’s best to avoid publishing AI-generated text verbatim.
Instead, use AI for things like
- Inspiration
- Outlines
- Titles & meta descriptions
- Researching statistics
Also, make sure to fact-check AI-generated information.
Here’s Google’s official stance on AI-generated content.
TIP: Enter the following prompt into a generative AI app like ChatGPT that accesses the web in real-time. You’ll typically get several nuggets of good advice.
Please compare this article https://yourcompany.com/existing-blog-post/ to the Google Helpful Content Guidelines https://developers.google.com/search/docs/fundamentals/creating-helpful-content and offer suggestions on how the content can be improved to meet the guidelines. Ignore the information in the article’s footer.
Include unique information
Your content will be more attractive to readers and, therefore, more interesting to Google if it includes some unique elements.
This type of content can be surveys or research data that people can’t find anywhere else. It could even be a unique perspective on a topic.
This approach will take longer, but it will help your content stand out in an ocean of mediocrity.
In March 2024, Elizabeth Tucker of Google wrote that Google will “reduce unoriginal content in search results.”
Do your topic and keyword research
Keyword research for your topic is still essential for any blog posts or pages you want people to discover through online searches.
Keywords are also called search terms — a ‘keyword’ is rarely one word.
Premium keyword tools include SEMRush, Ahrefs, and KWFinder. An up-and-coming keyword tool is KeySearch.
One approach is identifying moderate to high-volume, low-competition keywords related to your topic. For example, if your organization specializes in digital engagement using the Salesforce platform, “salesforce digital engagement,” on paper, would be a good keyword to target.
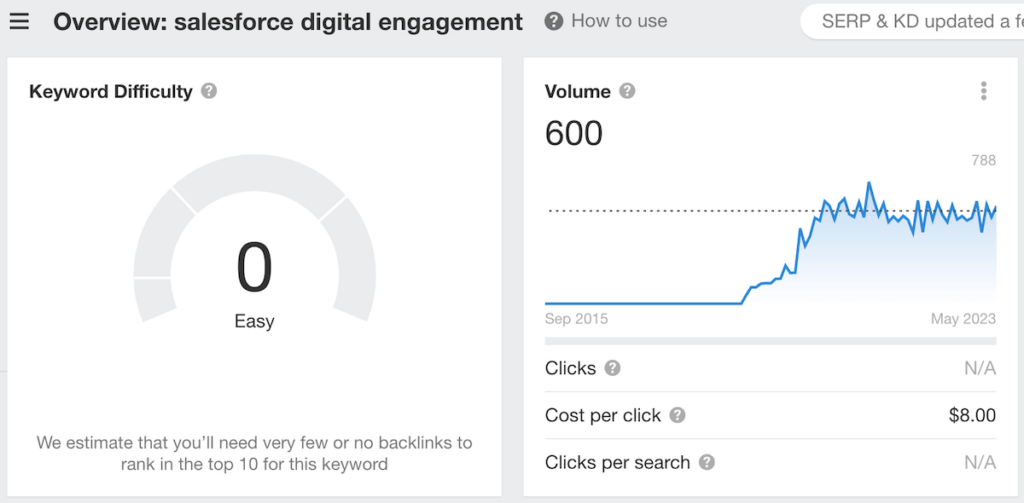
It’s also best to focus on at least three-word search terms. According to NP Digital, “If you remove brand queries, 77.91% of organic conversions come from search terms that are 3 or more words.”
Remember that helpful, well-optimized pages and posts can rank for dozens or hundreds of keywords.
If you create content for difficult keywords, don’t expect the content to be found through search. Instead, focus on keywords with good traffic potential and low difficulty.
Determine search intent
Before settling on a keyword, try to determine search intent.
In 2013, we published a blog post that continues to rank for the keyword “CRM administrator.” The post was intended to inform business managers and executives about the value of having a CRM admin.
However, based on the search results, that particular keyword attracts more job seekers than managers or executives. Here are the top 10 organic results for the keyword at the time this article was published:

Failing to consider search intent can mean attracting the wrong overall audience for your product or service.
Research semantically related keywords
Google’s Natural Language AI looks at more than a page or a post’s keyword. It also looks at all the words related to that keyword. It wants those related words to be in the proper context relative to the keyword.
Semantically related keywords are words that Google’s Natural Language AI has determined to be relevant to the main topic. Google refers to these as Entities.
Google provides developers with an API. Developers can create apps that feed content to the natural language understanding engine, which replies with how it interprets the words.
In our example above, Indeed.com may be able to rank higher for “CRM administrator” if it were to add more of the words in red from the following to its job listing:
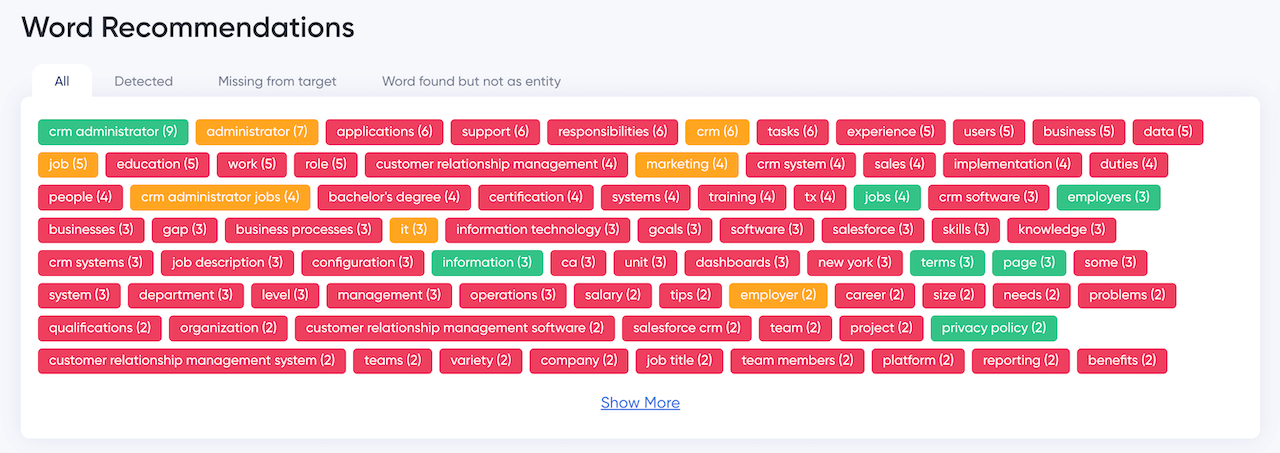
Recommended words like these need to appear within the content so that they read naturally.
SEO Tip: Google Search Console shows you pages with a low clicks-to-impressions ratio. Some of these pages may be candidates for adding more related keywords, which can positively impact SEO.
Get into the correct Google content category
Google’s NLU also uses category matches for ranking purposes. Google categorizes every page and post that it crawls.
Currently, there are over 600 content categories.
Your content is more likely to outrank other top-ranking content for a given keyword if your page or post is in the same category as the content you are trying to outrank.
To determine the top category, Google’s natural language engine analyzes words on an individual page and across an entire site.
Don’t spend too much time optimizing for advertisers’ keywords
There are specific topics for which ads are plastered at the top of the search engine result pages (SERPs). For example, if you search for “CRM software” or “accounting software,” you often won’t see the first organic search result until you scroll below the fold.
For keywords related to heavily advertised products and services, the juice might not be worth the squeeze. The number of ads will overwhelm the organic results.
On the other hand, if you decide to optimize for a common Google Ads keyword, you may still get clicks to your website from people who automatically scroll past ads.
Use a clean heading/subheading structure
Many website designers and bloggers overlook proper heading structure. Sometimes, website theme headings are used for design rather than structural purposes.
For better SEO, it’s essential to structure (or restructure) your pages and posts to have one H1 heading and multiple hierarchal subheadings (H2s and H3s) in the body text.
But it’s not uncommon for website pages to have multiple H1 headings. We have seen pages for which the designer used over 20 H1s.
Mechanically, changing to a proper heading structure is an easy SEO fix. This 𝕏-post has an excellent graphic that recommends the overall structure for a blog post.
Structure your URLs properly
By default, most content management systems create a blog slug (the last part of the URL) that incorporates the entire post title.
Google prefers brief and descriptive URLs and says that “users and search engines identify concepts in a URL more easily” when text is separated by hyphens rather than underscores.
For example, rather than using a URL like this:
https://www.example.com/customer-stories/How_Our_Software_Helped_Acme_Corporation_Increase_Its_Sales_By_100_Percent/
Use one like this:
https://www.example.com/customer-stories/acme-corp-sales-increase/
Optimize images
A common practice by website designers is retaining the original filename of a stock photo or the filename assigned by a digital camera or smartphone.
But keyword-rich filenames are an SEO opportunity.
Rather than using an image filename like this:
Depositphotos_33099063_L.jpg
Use one like this:
seo-strategy.jpg
Add alt text in your CMS editor using a variant of the image’s filename, such as “Your SEO Strategy.”
For page speed reasons (more on speed below), scale images to 1200 pixels wide. Then, compress the image using an app like TinyPNG.

SEO Tip: Whenever possible, use original photos rather than stock images. Google is okay with AI-generated images created with apps like Midjourney and ChatGPT.
Optimize off-page elements
Off-page mainly consists of a page or post’s meta tags. You can see these by selecting ‘View > Developer > View Source’ in Chrome.

You can still find homepage meta titles with the format ‘Company Name – Home.’ The title on a homepage and every other website page and post is a golden opportunity to inform people about what your company does when they read a snippet from your website in search results.
Remember that the on-page title people see when reading the page can differ from the off-page title, which appears in the search results.
Another important off-page meta tag is the Meta description. Even though Google rewrites the Meta description well over half the time, it’s worth adding descriptions to all your pages and posts.
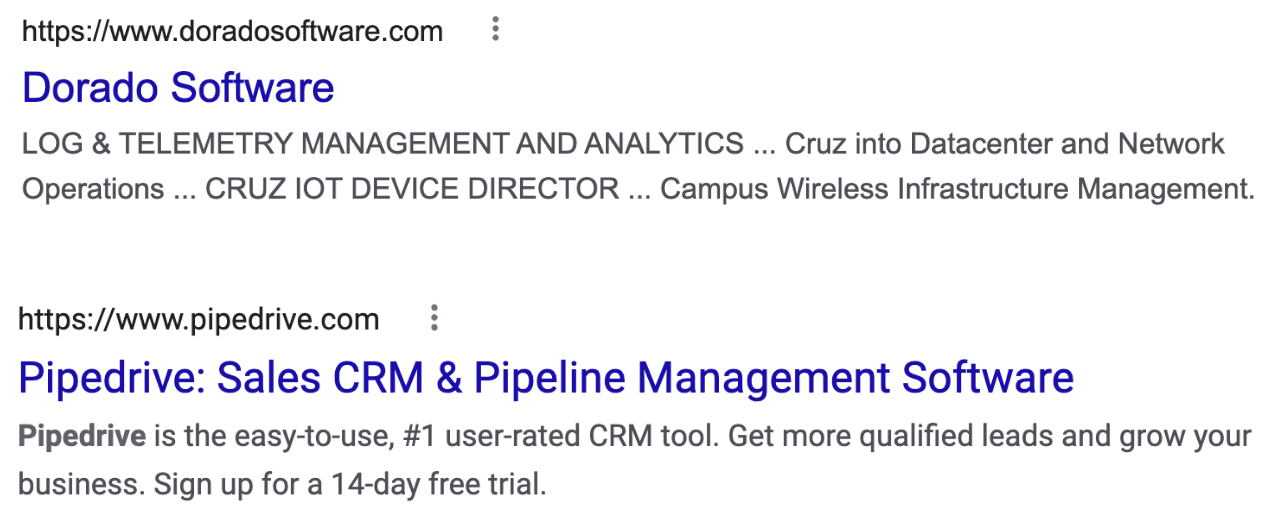
Notice the difference in the level of information between the following two Google search engine result snippets. The second one has a descriptive meta title and description.
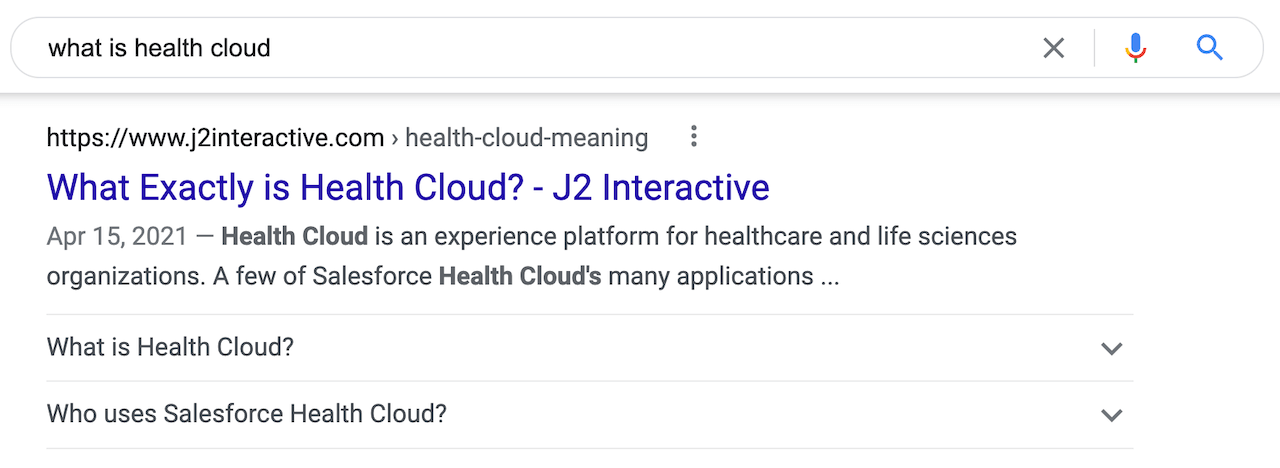
Structured data markup, such as FAQPage Schema, is another off-page element that can make your pages rank higher. FAQPage Schema involves having an FAQ section on a page and matching the questions and answers word for word, off-page, in a JSON-LD format.
Alternatively, you can use the Yoast FAQ block, as we did at the end of this post.
If you add this schema, you may see a rich snippet in the SERPs that makes your result stand out visually.
Acquire suitable backlinks
Google presented a slide to the U.S. Department of Justice, which included, “We do not understand documents. We fake it.”
Google can’t directly determine whether one article is better by reading two articles on the same topic. So, It has to rely on other signals, like quality backlinks.
The best backlinks are from websites with the most authority. One measure of authority is Ahrefs’ Domain Rating.
Think of backlinks as votes from the internet for your keywords.
The content category of the linking content is also essential.
If you plan to acquire backlinks using techniques such as targeted email outreach to improve SEO, target content that falls into the same Google category as the page for which you are trying to get a backlink.

An easy way to get quality backlinks is by creating and distributing content people want to link to.
Certain types of content lend themselves to organic backlinks. These include deeply researched articles and calculators.
Disavow certain purchased links
Many SEOs are now openly admitting that they pay for backlinks. However, most of these are a result of one-to-one outreach and are probably not detectable by Google.
However, if you purchased backlinks from link brokers in the past, consider disavowing those links.
Google announced a link spam update in December 2022 that targets sites with purchased links. It would be prudent to disavow any links you’ve purchased through brokers.
Add relevant internal links
If your website has a high-ranking page or post and you publish a new post on a related topic, link the former to the latter.
Those links can pass on authority from older pages to newer pages, which can result in more traffic—sooner—to your new pages.
One SEO case study suggests that having more internal links is better than fewer, but only to a point. Mixing up your internal anchor text is generally recommended.
Distribute your content
Distributing your content across social media, Google News, and your Google Business Profile (GBP) can prime the SEO pump.
Content distribution can drive awareness that may, in turn, result in additional quality backlinks.
You can also atomize your content — break it into smaller pieces before distributing it. Ross Simmonds is a guru of content distribution.
You can track referral traffic from various social platforms using Google Analytics.
Ensure your content is indexed
Your content cannot be found through a Google search until it is in the Google index.
It’s common for people to be unaware that some of their website’s content is not in the Google index.
Paste a URL into the top field in Google Search Console and hit ‘Enter’ to see if the page or post is in the Google index.
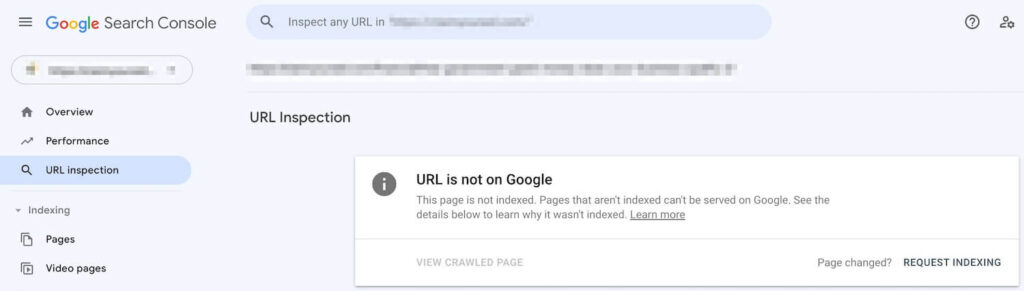
If the URL is not on Google, click ‘Request Indexing.’
If your site has a low Domain Rating, you may need to take other measures to get your content indexed.
Manage your content like other organizational assets
Helpful, well-optimized content can be a permanent asset to your organization. If you regard your website’s posts and pages as assets, they will get more attention.
Internally, we set up a marketing asset management system within our Salesforce org to help with content creation and re-optimization.
This allows tracking many data points for each piece of content and discovering ways to increase its online visibility.
Increase website speed & improve core web vitals
Your website’s performance factors into how a search engine regards your content.
You can use Google’s PageSpeed Insights to get a user experience report on both mobile and desktop.
If you’re designing a new website in WordPress, consider using the WordPress block editor plus a blocks plug-in instead of a third-party page builder. Regarding website speed, there is a beauty/bloat tradeoff to some degree.
Maintain your website’s health
A tool such as Ahrefs’ Site Audit, part of the company’s free Webmaster Tools offering, will give you an extensive report of website issues. The three categories are errors, warnings, and notices.
Error types include internal links from HTTPS to HTTP, broken internal links, broken images, too-large images, and 404 pages.
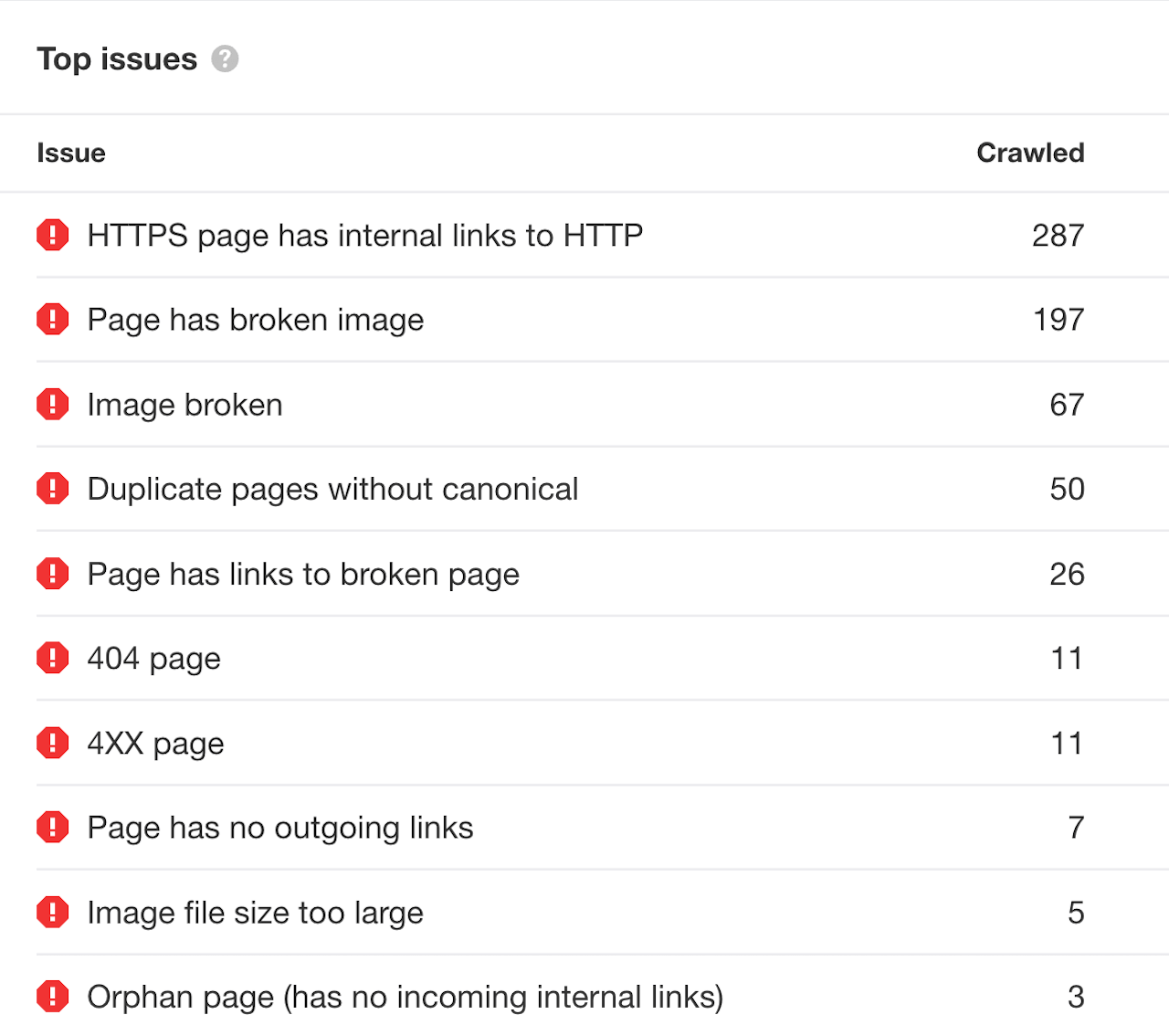
You will improve your website’s overall SEO by systematically fixing pages with errors and warnings.
Pay attention to spelling and grammar
Typos and grammatical errors can adversely affect SEO.
The free version of Grammarly and one of its browser extensions can improve SEO by alerting users to basic mistakes as they type within a browser tab.
Grammarly’s extension works with almost any text block within a browser tab, including website platform editors and Google Docs.
Consider readability
There are a variety of factors that make your writing more readable. Better readability can boost SEO.
These factors include using short sentences and paragraphs, enough transition words, and enough active voice.
Add canonical links
Canonical links are used to avoid issues that result from duplicate content.
A canonical link tells search engines which is the preferred or most authoritative page.
For example, if you have two nearly identical versions of a product page — one with U.S. spellings and one with U.K. spellings — you can add a canonical link that points from the U.K. version to the U.S. version.
Improved rankings in search engine results are often the sum of many things done right, particularly when trying to get your content to rank for competitive keywords.
If you spend time on enough of the little things and a few of the big things, you may be able to propel some of your content higher in the search engine results — in some cases, much higher.
You can convert more visitors into prospects and customers with the right conversion words and actions.
There are no guarantees when it comes to search engine optimization efforts. Google giveth and Google taketh away.
But if you consistently incorporate many or all of the above tips, you will better position your pages and posts in the eyes of search engines and improve site SEO.
Frequently Asked Questions
SEO is an acronym for Search Engine Optimization. It is a set of practices that, when applied, improve a website’s content relevance, link relevance, and technical setup. These practices make a site’s pages and posts easier to find through user search queries.
SEO aims to achieve a higher ranking in the search engine results for a query made by a prospective reader of your content or a buyer of your products and services.
Popular tools that require a subscription include SEMRush Keyword Magic Tool, Ahrefs Keywords Explorer, Keyword Keg, and Wordtracker. These are all excellent sources of keywords, but the features vary among vendors.
If you have full editing rights to your website, you can make a range of changes to existing on-page and off-page content to boost your website’s SEO.
It’s best to use an AI writer for inspiration and guidance. Using AI-generated content word-for-word may produce short-term results but not long-term if the search engines detect the content as AI-written.